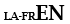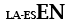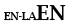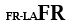|
|
 Identification
Identification
|
| Official Latin term |
plexus enterici ganglionares 
|
| Official subsidiary term |
ganglionary enteric plexus 
|
| Unit identifier | TAH:U6856 |
| Unit type | unit type set |
| Materiality | material |
 Navigation
Navigation
|
 Notes
Notes
|
| The enteric aganglionic plexuses are networks of nerve fibres consisting of axons and enteric glia but without regular nerve cell bodies. They exist in the mucosa (Plexus aganglionaris mucosus), in the muscularis mucosae (Plexus aganglionaris muscularis mucosae), in the two layers of the muscular coat (circular and longitudinal muscle plexus: Plexus aganglionaris internus muscularis and Plexus aganglionaris externus muscularis) and underneath the serosa (serosal plexus; Plexus aganglionaris serosus). The extreme aganglionic plexus (Plexus aganglionaris extremus) is situated directly at the innermost border of the circular muscle, between the ganglionic external submucosal plexus and the inner border of the circular muscle. Some authors add this plexus to the circular muscle plexus (Brehmer A, Rupprecht H, Neuhuber W 2010 Two submucosal nerve plexus in human intestines. Histochem Cell Biol 133:149-161). |
 Partonomy
Partonomy
|
| TAH:E10200 |
 corpus humanum corpus humanum 
|
| TAH:U5062 | |
| TAH:U6322 | |
| TAH:U6758 | |
| TAH:U7697 | |
| TAH:U6856 |
 plexus enterici ganglionares plexus enterici ganglionares  TOT TOT
|
| TAH:U6859 |
| TAH:U9571 | |
| TAH:U9555 |
| TAH:U6858 |
| Total |
4 children
|
 Taxonomy
Taxonomy
|
| FMA:62955 | |
| FMA:61775 | |
| FMA:67165 | |
| FMA:305751 | |
| FMA:67135 | |
| FMA:49443 | |
| FMA:5898 | |
| FMA:5901 | |
| FMA:5910 | |
| FMA:77597 | |
| TAH:G6856 |
 plexus entericus ganglionaris plexus entericus ganglionaris 
|
| Total |
2 children
|
| Date: 25.06.2025 |